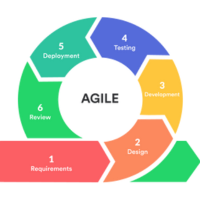
How agile teams stay organized with ceremonies and frameworks

Agile is all about flexibility, but that does not mean teams work without organization. To stay aligned, productive, and continuously improve, Agile teams follow structured routines called ceremonies. These ceremonies provide opportunities to plan work, track progress, and reflect on how to get better.